
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause episodes of pain. When these episodes occur, there are things you can do to manage the symptoms.
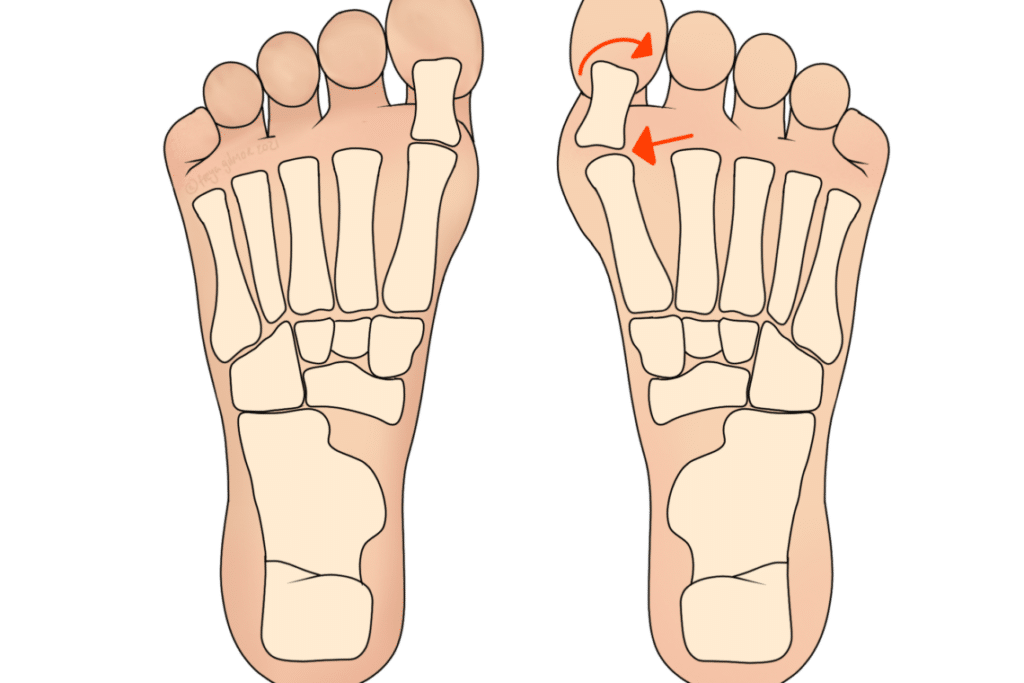
A bunion is a soft tissue swelling on the outside of the foot at the base of the little toe. This joint is the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (1st MPJ). More specifically, the exact area affected is the metatarsal head. This part of the foot does stick out slightly in everyone, but is more prominent with a bunion.
Over time, the swelling will progress to misalignment of the joint, with the toe pointing into the rest of the foot. The swelling looks larger, as the joint begins to push outwards. Symptoms can include redness over the area, a callus, and tenderness. Symptoms may come and go over months or years.
Inappropriate footwear is a significant factor in the development of bunions. Pressure on the joint from tight fitting or high heeled shoes can cause enough irritation to start the process. It is also possible for local trauma to cause the initial irritation. Another name for the condition is “tailor’s bunion” in reference to the pressure of sitting cross-legged as a tailor might.
Some people are more predisposed to developing the condition due to their anatomy. If the 5th MPJ naturally sticks out (and the toe points in), they may be more likely to irritate the area. There is also a strong genetic link.
The small joints of the feet are among those most commonly affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis. For people with RA, bunions can be harder to manage. Joints affected by rheumatoid conditions like these need frequent, gentle movement. Prolonged rest or excessive exercise will aggravate symptoms.
Typical advice for an aggravated bunion is to rest and ice it. Some people also find that a bunion cushion or pad can help take some pressure off. Rest and ice are measures used temporarily to manage acute symptoms. They aim to reduce redness and swelling, but it is important not to over-ice. Rest is also only beneficial in the short term- healthy movement will do more for the joint than keeping it still over a longer period.
Sometimes a bunion is caused by supination (or under-pronation) of the foot. That means that your foot has rolled out, and often comes with higher arches. Walking like this puts direct pressure on the area a bunion may form. Your osteopath can look at the way you walk to determine what has caused this supination, and address it with treatment if appropriate.
Your osteopath can give you advice beyond the standard recommendations:
Exercises may be useful to keep the small joints of the foot mobile.
Book an appointment here to start managing your bunion.